

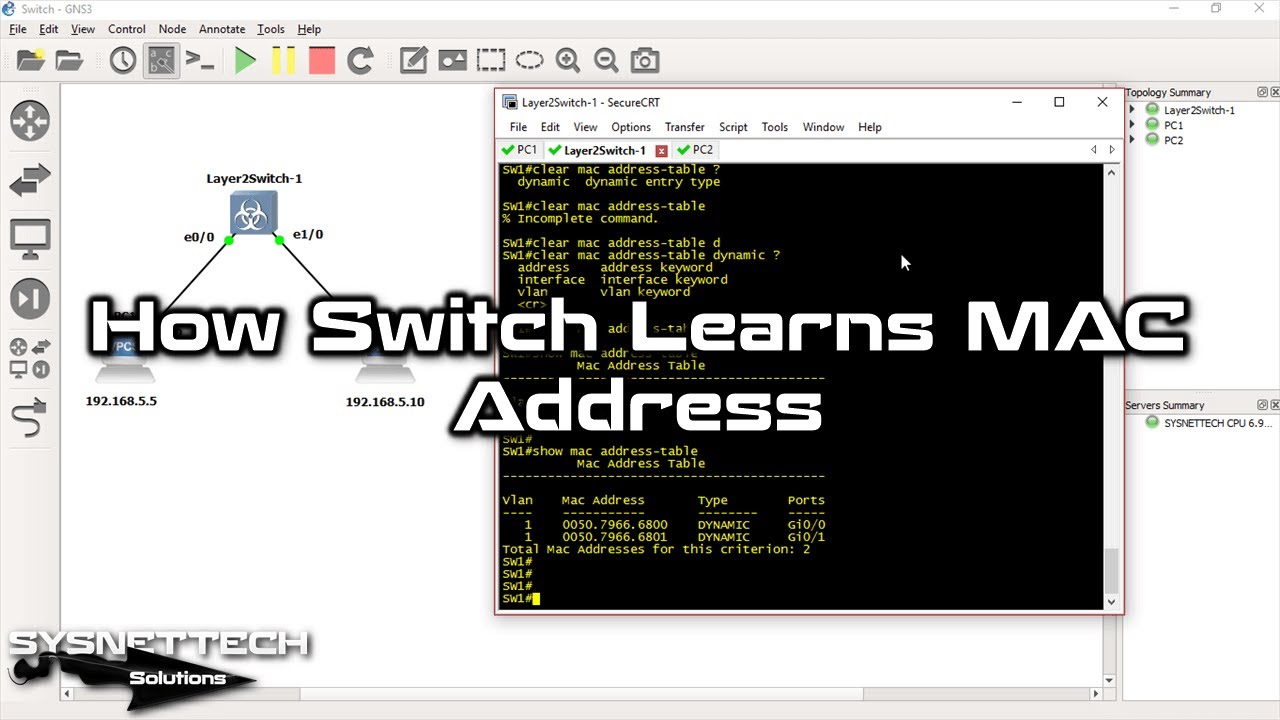
The customer is allocated VLAN 10 (outer VLAN tag).Įnter configuration commands, one per line. Normally your switch will automatically learn MAC addresses and fill its MAC address table (CAM table) by looking at the source MAC address of incoming frames. A Layer 2 protocol tunnel is enabled for STP BPDUs.

This example shows a service provider switch that is configured to process Q-in-Q for traffic coming in Optionally, you can also add one of these combinations. MAC address learning for Q-in-Q tagged packets is based on the outer VLAN (Service ProviderĬonfiguration Examples for Q-in-Q and Layer 2 Protocol Network nodes with multiple network interfaces, such as routers and multilayer switches, must have a unique MAC address for each NIC in the same network. (OPTIONAL) Enter the keyword dynamic to display only those MAC addresses the switch dynamically learns. You should only see the outer mac address in your mac address table, Can you post your config? The default can be changed to any value between 1 and 3,000. In any case, a switch does not need an entry in its MAC address table to be able to get a frame to the destination it is just much more efficient to do it that way.I don't know what u/Daeloan get his information from. 10 0 The maximum number of secure MAC addresses that can be configured in Cisco Catalyst switches when port security is configured TCC2 Advocate Options 06-22-2009 04:46 PM - edited 03-01-2019 04:02 PM Resolution A secure port has a default of one MAC address. A MAC address, also known as hardware address or physical address, is a binary number used to uniquely identify computer network adapters. This prevents dead hosts from using switch resources, and it facilitates moving a host from one interface to another on the same of different switch. 1) sticky + static Switch1 (config-if)switchport port-security mac-address sticky H.H. What you want to do requires something connected to the server's switch interface to send a frame into the switches, but it will need to happen on a regular basis because entries in a switch MAC address tables are dynamic and time out. Message Switching provides a dynamic routing as the message is routed through the intermediate nodes. Switches will flood unknown unicast MAC addresses (those not in its MAC address table) to every switch interface A frame sent by Host2 will be delivered to the server, but it will do that by being sent to every switch interface, much like a broadcast or multicast frame. The destination address is appended to the message. Based on your comments, you do not seem to understand that any frames sent to that MAC address will arrive on that switch interface, regardless of whether or not the switch has the MAC address in its MAC address table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
